Table of Contents
ToggleChlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections, often lurking silently in the body without noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do appear, they can manifest in various ways, including the emergence of bumps on the inner thigh. These bumps can be alarming and may lead individuals to seek answers about their health.
Understanding chlamydia and its potential effects is crucial for maintaining sexual health. While bumps on the inner thigh can stem from various causes, recognizing the signs and seeking timely medical advice can make all the difference. This article explores the connection between chlamydia and skin manifestations, providing clarity and guidance for those concerned about their symptoms.
Overview of Chlamydia
Chlamydia constitutes a widespread sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. This infection frequently remains asymptomatic, leading to unnoticed transmission. When symptoms present, they may manifest as bumps on the inner thigh, urethral discharge, or pelvic pain.
Chlamydia primarily spreads through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Affected individuals can unknowingly transmit the infection to sexual partners. Without treatment, chlamydia can result in serious health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility.
Diagnosis occurs through various tests, including urine tests and swabs from affected areas. Healthcare providers recommend regular screening for sexually active individuals, particularly for those with multiple partners or a history of STIs.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, effectively eliminating the infection in most cases. Timely medical intervention significantly reduces the risk of complications. Regular follow-ups ensure the infection has cleared and prevent reinfection. Understanding chlamydia’s implications for sexual health is essential for informed decisions regarding prevention and care.
Symptoms of Chlamydia
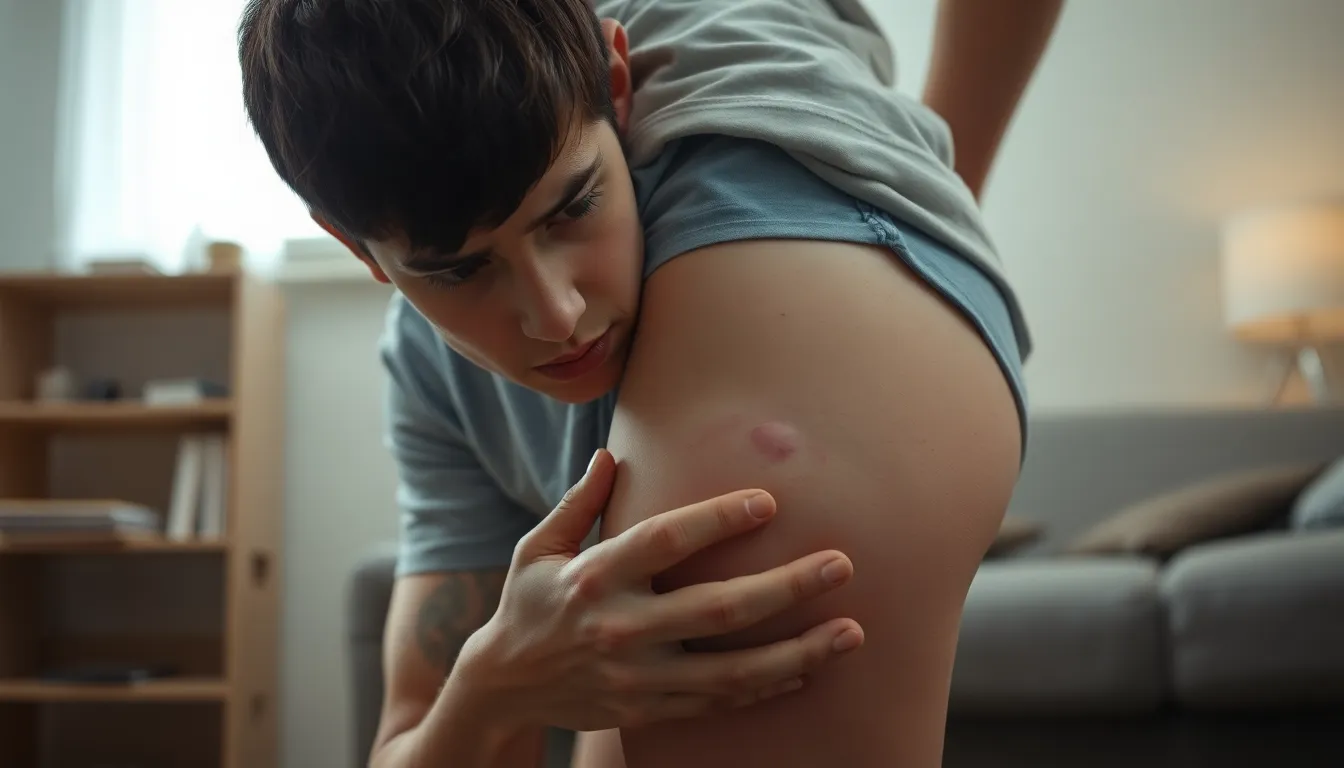
Chlamydia can manifest in various ways, including bumps on the inner thigh and other areas. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Chlamydia Bumps
Chlamydia bumps often appear as small, raised lesions on the skin. These bumps can occur anywhere on the body but are typically found in sensitive areas like the inner thigh. While bumps can indicate an infection, they might also result from other skin conditions. It’s essential for individuals to monitor changes in their skin and seek medical evaluation if they notice new lesions or other concerning symptoms.
Other Symptoms to Watch For
Chlamydia presents additional symptoms beyond bumps, including:
- Urethral Discharge: A noticeable discharge from the penis or vagina can occur, often described as cloudy or abnormal.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the pelvic region is common, especially during intercourse or urination.
- Burning Sensation: A burning sensation while urinating can indicate irritation or inflammation caused by the infection.
- Abnormal Bleeding: Women may experience irregular bleeding between periods or after sexual intercourse.
- Testicular Pain: Men might notice pain or swelling in the testicles, signaling potential complications.
Recognizing these symptoms enables timely medical attention, reducing the risk of complications associated with untreated chlamydia.
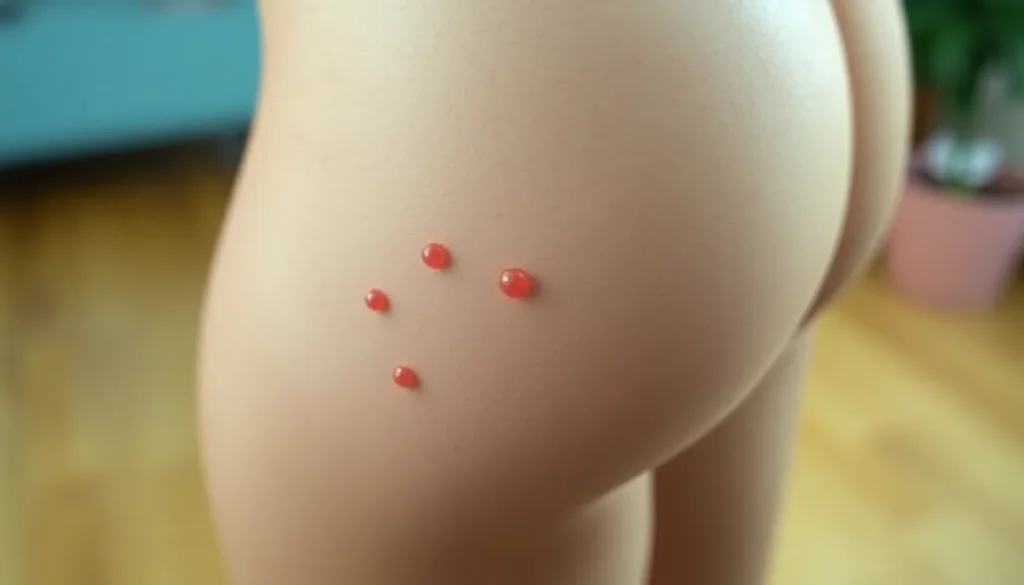
Chlamydia Bumps on Inner Thigh
Chlamydia bumps on the inner thigh may appear as small, raised lesions or sores. These bumps can vary in size and can be a sign of the infection manifesting on the skin.
Appearance and Characteristics
Chlamydia bumps typically present as red or flesh-colored, round lesions on the inner thigh. The texture may range from smooth to slightly rough, and they can be painless or tender upon touch. These bumps may coincide with other symptoms, such as urethral discharge and burning during urination. They can also appear alongside other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), making accurate identification essential.
How They Differ from Other Skin Conditions
Chlamydia bumps differ from other skin conditions by their association with sexual transmission and potential accompanying symptoms. Unlike common skin irritations or infections such as folliculitis or ingrown hairs, chlamydia bumps often indicate a systemic infection that necessitates medical evaluation. Additionally, other STIs, like herpes or genital warts, may present similar symptoms but often include other unique features, such as blistering or cauliflower-like growths. Proper diagnosis through a healthcare professional is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosis of chlamydia involves a combination of laboratory tests and clinical evaluations. Healthcare providers typically utilize the following methods for accurate testing:
- Urine Test: Individuals provide a urine sample to detect the presence of Chlamydia trachomatis. This method is non-invasive and relies on nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) for high sensitivity.
- Swab Test: For those presenting with genital symptoms, clinicians may perform a swab of the urethra, cervix, or other affected areas. This procedure aids in identifying the bacteria and assessing associated infections.
- Pelvic Exam: Physicians may conduct a pelvic examination to evaluate any signs of infection in women. This exam helps identify complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Regular Screenings: Healthcare professionals recommend regular screenings for sexually active individuals, particularly those with multiple partners or a history of STIs. Routine testing enables early detection and treatment, reducing transmission risk.
It’s crucial to understand that symptoms alone do not confirm chlamydia. Laboratory testing provides definitive diagnosis. Prompt testing allows for timely treatment, preventing long-term health issues like infertility or chronic pelvic pain.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for chlamydia bumps on the inner thigh primarily involves medical interventions and preventive measures. Both medical treatments and home remedies may aid recovery or alleviate some symptoms.
Medical Treatments
Healthcare providers commonly prescribe antibiotics such as azithromycin or doxycycline to treat chlamydia infections. Azithromycin is typically given as a single dose, while doxycycline requires a week-long regimen. These medications effectively eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Individuals must complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing them. Follow-up testing is essential to confirm the infection’s resolution. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend a re-test after three months to ensure there is no reinfection.
Home Remedies
While antibiotics are the primary treatment for chlamydia, some home remedies may support symptom management. These include:
- Warm compresses: Using warm compresses on affected areas may help reduce discomfort and inflammation.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids supports the body’s natural healing processes.
- Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can strengthen the immune system.
Home remedies serve as complementary methods and should not replace professional medical advice or treatments. Individuals experiencing symptoms should consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate medical care.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing chlamydia effectively involves several key strategies that reduce the risk of infection.
- Utilizing Barrier Protection: Employ condoms or dental dams during sexual activity. Consistent use significantly lowers the likelihood of transmitting STIs, including chlamydia.
- Limiting Number of Sexual Partners: Maintain monogamous relationships or limit the number of sexual partners. Fewer partners result in reduced exposure to potential infections.
- Regular STI Screenings: Schedule routine screenings for STIs, especially for sexually active individuals with multiple partners. Early detection enhances treatment efficacy and minimizes infection spread.
- Complete Treatment Regimens: Adhere to prescribed antibiotic treatments and ensure sexual partners receive treatment as well. Completing the medication course minimizes recurrence and complications.
- Open Communication: Discuss sexual health openly with partners. Transparency about STI testing and sexual history encourages responsible sexual practices and awareness.
- Educating About STIs: Become informed about chlamydia and other STIs, their symptoms, and transmission routes. Knowledge empowers individuals to make safer choices regarding sexual activity.
Implementing these strategies works to protect individual and partner health, ultimately reducing the prevalence of chlamydia and promoting overall sexual well-being.
Conclusion
Chlamydia bumps on the inner thigh serve as a critical indicator of a potential infection. Recognizing these symptoms can prompt individuals to seek timely medical evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital in preventing serious health complications.
Maintaining open communication about sexual health and engaging in regular screenings are essential steps in safeguarding one’s well-being. Individuals should not hesitate to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment options. Prioritizing sexual health education and awareness can empower individuals to make informed choices and reduce the risk of STIs.




